LEADING INDIAN STATES
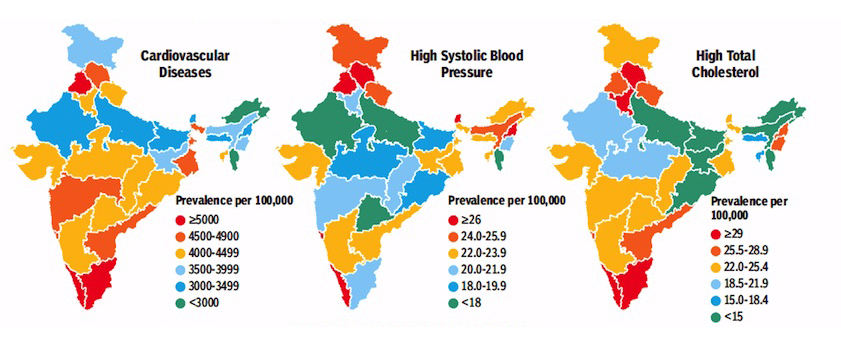
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in 2016 was the highest in Kerala, Punjab and Tamil Nadu i.e. more than 5,000 per population of 100,000. Andhra Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, Goa and West Bengal are close second with prevalence between 4,500 and 4,999 per 100,000.
As a matter of concern, heart diseases are projected to account for 35% of the deaths amongst India’s working age (20 to 60) population between 2020 and 2030, as per the ICRIER study.
DID YOU KNOW?
Case-control studies have reported that important risk factors for CVD in India are dyslipidaemias, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, abdominal obesity, psychosocial stress, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity along with genetic predisposition.